There has been much debate in recent years as to the relationship between Bonsai and Art. Is the practice of Bonsai purely horticultural or does it have strong artistic aspects as well?Many enthusiasts initially approach bonsai for its horticultural practices and it is only when they then attempt to style and form their trees, that the artistic and creative side of the practice comes into play.There are in fact many basic artistic principles at play when we design our trees; or, at least there should be. Many of these principles are already applied to bonsai for us in the often cited ‘Rules (Guidelines) of Bonsai’.This article deals with one of the most important and basic principles in Art known as ‘The Golden Section’.
THE GOLDEN SECTION
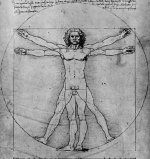
The Golden Section is a Law of Proportionality. It is a Law that occurs frequently in nature and its use is particularly useful in Art. First developed by Vitruvius, it is most famously known from Leonardo Da Vinci’s 1509 drawing ‘The Divine Proportion’.
Essentially the law states that two unequal parts of a whole must be in relationship to each other to create a satisfactory image to the eye.Numerically, the Golden Section is approx. 1.618034 or the ratio 38%-to-62%. This proportion reoccurs throughout our lives and is said to create an ideal proportion between two objects or two parts of a whole.
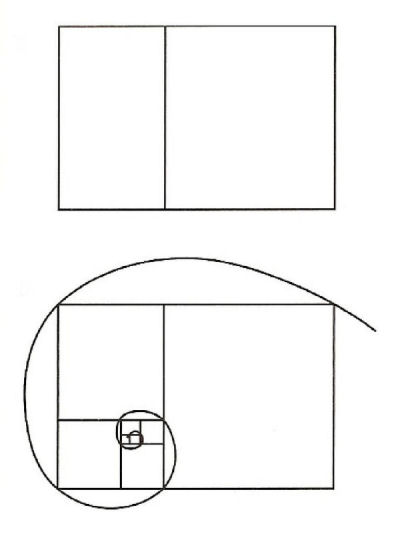
The above diagrams show the Golden rectangle, divided into two parts using the Golden Section ration of 38%/62%. Followed by the golden spiral. This is where the spiral is marked out traversing successive edges of golden section rectangles. This exact spiral exists in many natural forms such as in seashells and plants.
The naturally occurring Golden Section proportion/ratio reoccurs throughout our lives. For instance the proportion between our forearms and upper arms is 38% to 62% and the same ratio applies between our hands and forearms. Our own faces are comprised of this ratio; within the relationships between our eyes, ears, mouth and nose, the Golden Section can be found. Further (conscious or subconscious) recognition of the Golden Section in inanimate and artistic endeavours therefore feels ‘right’ to the eye and creates a feeling of satisfaction and harmony within an image.
The Golden Section ratio also appears in what is known as the Fibonacci Series. This is a sequence of numbers where each number is the sum of the two preceding numbers: 1 1 2 3 5 8 13
The ratio of two successive numbers in this sequence is approximately equal to the Golden Section.
0+1=1
1+1=2
1+2=3
2+3=5
3+5=8 …
This is called the Fibonacci sequence. This numerical sequence can be frequently occurring in nature. For example, the flower of a rose will have spirals of 3 petals in one direction, and 5 petals in the other.

A pine cone will have 3+5=8 spirals in one direction and 5+8=13 spirals in the other.
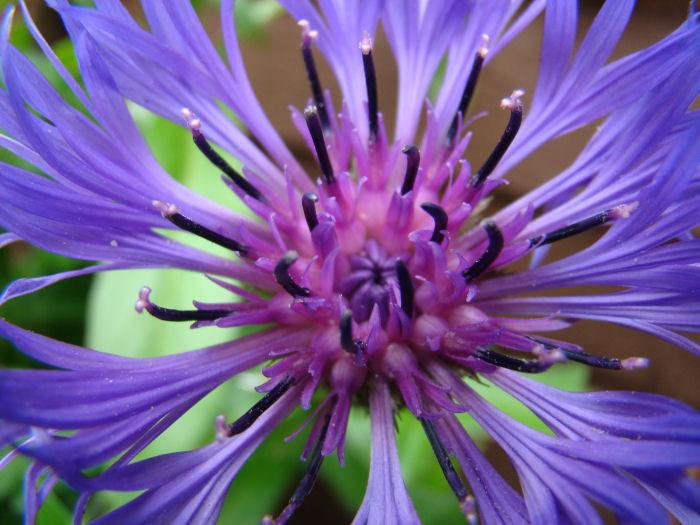

This Cornflower has a ring of 8 stamen around its centre surrounded by an outer ring of 13 stamen (image courtesy of Claire Simpson)
Finally, the Golden Section gives rise to the ‘Two Thirds Rule’ within art and particularly Asian art. It involves creating a place of emphasis or focus within the composition. The point of emphasis is found by dividing the painting into three parts vertically and then horizontally; where the dividing lines meet (there are four points) are supposedly aesthetically pleasing places to put the focus of the painting. From an evolutionary psychological perspective, the aesthetic aspect of this form of composition could be justified. It is not natural to have objects perfectly centred and symmetrical.

The above painting has been divided into thirds in accordance to the ‘Two Thirds Rule’ and the Golden Section. This composition creates harmony to the eye because the main focus points are placed along aesthetically pleasing lines, the objects are asymmetrically placed according to the ratio.
The Golden Section appears time and time again within Bonsai guidelines. Every time two design elements are placed in conjunction to each other, there is an opportunity to satisfy the rules of the Golden Section.Since we are dealing with living plants or materials that are constantly changing through the seasons, the Golden Section is simplified to a ration of 1:2/3 or 1½:1From the dimensions of the pot in relation to the bonsai, the distances between each branch level as it ascends up the trunk of the tree, to the position of planting within the pot, the Golden Section is often applied.The asymmetry of the Golden Section is used throughout the Art of bonsai; from avoidance of symmetrical positioning and asymmetrical triangular patterns to the use of odd (rather than even) numbers.
How many times have we heard that the first branch should be placed at a level 1/3 of the height of the tree? That the tree should be planted towards the left or right and not in the centre of the pot? That a bonsai should be placed towards the left or right and not the centre of a display stand? That the main tree within a group planting should never be placed in the centre of the pot?

As an example of the way that the Golden section can be applied to a very simple picture; here is a formal upright tree with the first branch positioned 1/3 of the height of the tree. Each branch is placed with diminishing spacing between it and the next branch according to the Golden Section.

In this image the first branch has moved downwards; its relationship visually with the tree as a whole and the next branch upward has changed and creates a less restful image. This is not necessarily ‘wrong’, however it is now undeniably a less ‘restful’ image than before.

Finally, three branches have been moved up and downwards though the first branch is correctly positioned according to the Golden Section. The image has now become visually uncomfortable.
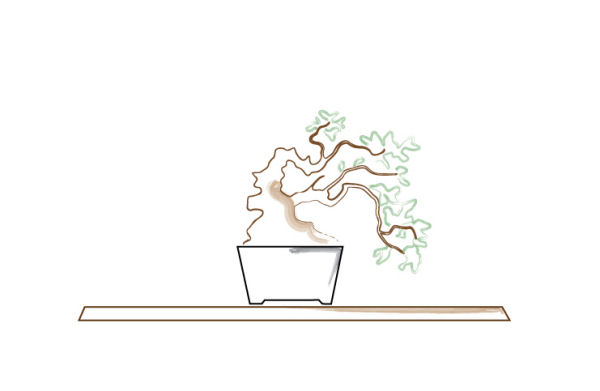
A second example, in this image, the bonsai (as a whole) is placed centrally on its stand.
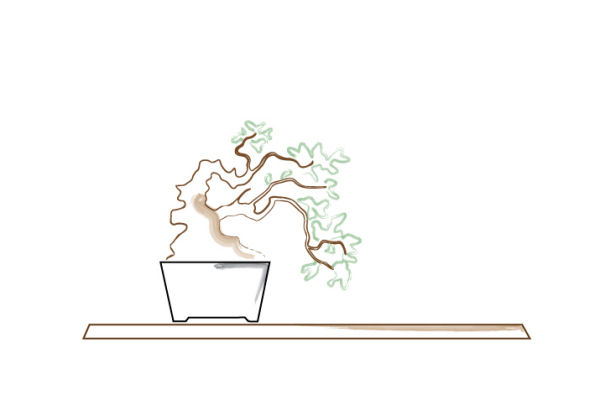
It is not until the bonsai is placed according to the rules of the Golden Section and the Two Thirds Rule, that the image as a whole is resolved.
FINALLY……
Through this relatively simple law, much of the way we can create and perceive Art can be altered. In one article it would be impossible to cover all the far reaching implications of the Golden Section within just the context of bonsai, let alone Art itself. By understanding the principles of the Golden Section it is possible to positively apply them in a myriad of ways when styling and presenting your trees.
However, it should be noted that it would never be possible for every facet of a tree to comply with the Golden Section, neither would it be beneficial to try to. Trees, trunks and branches do not grow in accordance with an Artistic Law and its over use within a composition could well become too visually repetitive.
Certain features within a design that disobey the Golden Section can be deliberately used to create movement and energy which is then resolved elsewhere in the composition.


